Do You Need a Reviewer for Setting Up Computer System Access Fda
COMPUTER SYSTEM VALIDATION MASTER Program
| Document No. | |
| Version No. | 00 |
| Effective Date | |
| Review Engagement | |
| Total No. of Pages |
INDEX
| S. No. | Content | Page No. |
| 1.0 | Approving sheet | |
| two.0 | Introduction | |
| 3.0 | Objective | |
| 4.0 | Computerized Systems Validation Policy | |
| 5.0 | Scope | |
| 6.0 | Definitions | |
| 7.0 | Role and responsibilities | |
| 8.0 | Identification And Categorization of Computerized Systems | |
| 9.0 | Validation Strategy and Deliverables | |
| 10.0 | Supplier Cess | |
| 11.0 | Quality Run a risk Management | |
| 12.0 | Validation Requirements | |
| thirteen.0 | Documentation | |
| 14.0 | Alter Control | |
| 15.0 | Training | |
| 16.0 | Maintenance and Support | |
| 17.0 | Document Completion Process | |
| eighteen.0 | Arrangement Retirement | |
| 19.0 | Project Activities Monitoring, Controlling and Reporting | |
| 20.0 | References | |
| 21.0 | Annexure | |
| 22.0 | Abbreviation | |
| 23.0 | Revision History |
- Approval Sheet:
Prepared by:
| Proper name | Designation-Department | Signature | Appointment |
Reviewed by:
| Proper noun | Designation-Department | Signature | Appointment |
Canonical by:
| Name | Designation-Department | Signature | Date |
Authorized by:
| Name | Designation-Section | Signature | Engagement |
- INTRODUCTION:
The complexity of processes, management of data and its repeated use is the driving strength for automation of processes using computerized system. The systems take the advantages of online data cosmos, review, approval, archival, retrieval, storage, utilization and helps to reduce the overall resource required for newspaper-based data management.
Definiteness in operation and performance of these computerized systems becomes an important consideration since they manage the processes and will direct or indirectly impact consistency, reliability, accuracy of data, product quality, patient rubber and data integrity.
The compliance of these systems to GxP and regulatory requirements tin exist assured just if a life cycle approach is planned for systematic and documented planning, development, validation, implementation and post implementation activities.
This principal plan and the attachments shall be used as a framework for the life bicycle approach for managing computerised systems.
- OBJECTIVE: The Objective of this policy is to :
- Provide directives to develop the private Electronic System Plan.
- Generate Records to provide testify of being in compliance with regulatory requirements.
- To ensure that Arrangement is fit for intended utilise.
- To identify and ascertain roles and responsibilities of key individuals during the acquisition,development, validation and deployment process; and
- Spread awareness to the audition on the diverse aspects of conquering, development, validation and deployment of electronic systems.
- COMPUTERIZED SYSTEMS VALIDATION POLICY:
The Computerized Systems Validation Policy specifies that,
- This Policy is owned by the Head-Quality;
- All electronic systems, procured or adult shall attach to this policy;
- Any exception or departure to this policy need to be documented and approved.
- Computerized systems validation is important to ensure compliance with regulations and to achieve business benefits;
- Management supports estimator system validation as a business organisation critical activity;
- All systems within the scope used in regulated environments shall be validated. The extent of validation shall depend on the adventure, which the system has on Product Quality, Patient Safety, Information confidentiality, Data Integrity and Business organization Continuity and shall as well depend on the type and complexity of the system;
- Validation Team shall include personnel from various disciplines based on the employ of the system;
- Take chances Based arroyo can be taken to optimize and focus overall efforts towards the Estimator system validation procedure;
- SCOPE:
This policy is applicable for computer organisation validation at ______________________
The Computerized System Validation Chief Plan applies to all computerized systems which are used to perform and support GxP regulated activities. Consequently, there may be systems, whose operation, although important for the efficient and economic operation of the facility, cannot be considered critical to the quality of production and therefore will not be validated as part of this activity.
- DEFINITIONS:
- Qualification: Qualification is the act of planning, executing and recording of tests on equipment and systems, which form part of the validated process, to demonstrate that information technology works correctly and leads to the expected results.
- User Requirement Specification (URS): A requirement specification that describes what the equipment or system is supposed to do, thus containing at least a set of criteria or conditions that have to be met.
- Functional Specification (FS): Specifications that document functions, standards and permitted tolerances of systems or organisation components and which define the operating capabilities of the equipment/ organization.
- Design Specification (DS): Systems pattern is the process of defining the compages, components, modules, interfaces, and data for a system to satisfy specified requirements.
- Installation Qualification (IQ): Installation qualification is a documented verification that the systems as installed or modified, comply with the canonical design and manufacturer's recommendation.
- Operational Qualification (OQ): Operational qualification is a functional testing to ensure that each component of a system perform as intended inside the representative/ anticipated operating ranges co-ordinate to Functional specification.
- Performance Qualification (PQ): Operation qualification confirms that the system is capable and performing/controlling activities of the processes as intended according to URS in a reproducible manner while working in specified operating environment, which includes hardware arid software of the computer system.
- Validation Protocol: The validation protocol is a written plan, stating how validation will be conducted, with roles and responsibilities of validation squad, deliverables including examination parameters, organization characteristics, device checks and determination points on what constitutes adequate test results.
- Validation Report: The validation report is written report on the validation activities, the validation data and the conclusions drawn.
- Re-validation: Repeated validation of an approved system (or a part thereof) to ensure continued compliance with established requirement.
- Risk Management: A systematic process for the assessment, command, communication and review of gamble to quality.
- Take chances Assessment: It is a systematic method to assess and characterize the critical parameters in the functioning of a system.
- Computer System: A figurer is a device that accepts information in the course of digitalized information and manipulates information technology for some consequence based on a program or sequence of instructions on how the data is to be processed. A system including input of data, electronic processing and output of data to be used either for reporting or automatic control.
- Computerized System: A computerized system consists of hardware, software and network components which together fulfill certain functionalities. It tin can also be defined as a logical entity partially or entirely controlled past computers but may likewise include some equipment, utilities, sensors & actuators along with the governing procedures. For example Building Management Organization; Automated manufacturing / Laboratory Organisation; Document Management Organization; etc.
- Computerized Organization Validation: Information technology is a procedure of achieving and maintaining compliance with applicable GxP regulations and fitness for intended employ of computerized systems.
- Commercial Off-the-Shelf Software (COTS): Software divers by a market place driven need, commercially bachelor, and whose fitness for use has been demonstrated by a broad spectrum commercial users.
- Electronic Signature: A computer data compilation of whatever symbol or series of symbols executed, adopted, or authorized past an individual to be the legally binding equivalent of the private'south handwritten signature.
- Electronic Records: Any combination of text, graphics, information, audio, pictorial, or other information representation in digital form that is created, modified, maintained, archived, retrieved or distributed by a reckoner system.
- Open Systems: An environment wherein system admission is not controlled by person/s, responsible for the content of electronic records on the system.
An open up system is a arrangement which allows application portability, arrangement interoperability, and user portability between many unlike reckoner vendor hardware platforms.
A closed system is vice-versa to the to a higher place.
- Airtight Systems: An surroundings wherein arrangement access is controlled past person/southward, which are responsible for the content of electronic records on the system.
- Configured Arrangement: Configured systems are those which consist of standard system components and that enable configuration every bit per user requirement (the basic software is coded for general purpose and not as per specific client requirement).
- Bespoke Systems / Customized Arrangement: Customized systems are those systems which consist of system components which are developed to run into specific needs of customer.
- Legacy System: Legacy systems are regarded as systems that have been established and in use for some considerable time.
- GxP Regulation: The underlying international pharmaceutical requirements, such as those set forth in the US FD&C Act, US PHS Act, FDA regulations, EU Directives, Japanese regulations, or other applicable national legislation or regulations under which a company operates. These include but are not limited to:
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
- Adept Laboratory Practices (GLP)
- Good Distribution Practices (Gross domestic product)
- Good Technology Practices (GEP)
- GxP Compliance: Meeting all applicable pharmaceutical and associated life science regulatory
- Network: A system (manual channels and supporting hardware and software) that connects several remotely located, computers via telecommunications and allows information and resource sharing (hardware and software) between different computers along with data transfer to distributed workstations.
Example: Personal Area Network, Local Expanse Network, Wireless Local Area Network, Broad Area Network.
- ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES :
Specific organizational structure is responsible for proper distribution of work to reach the validation target. Following roles and responsibilities shall be followed by individuals and teams in the validation procedure.
- Validation team:
- This team shall comprise of members from the following and/ equally required.
Organisation Possessor/User Department, Quality Assurance, It, Technology, System provider and/ or Outside validation agency.
| Function | Responsibility |
| System Owner/User | a. Ensuring that all software and computer systems in the section are listed in the listing. b. Managing alter control and escalating issues where necessary. c. Ensuring that all systems in the department are validated according to the projection plan/ Validation programme. d. Ensuring that QA and It are notified earlier purchase of new systems. e. Providing detailed and complete fix of requirements in a documented form. f. Providing resources for functional and performance testing g. Preparation/ Review of validation protocol/ report h. Providing user expertise inputs in the creation and review of validation deliverables. i. Ensuring that SOPs are adult covering employ of the system and contingency situations and arrangement recovery in case of system failure. j. Ensuring adequate training for the users. |
| Engineering | Responsible for following activities related to Procedure Control Systems: a. Managing validation/projection deliverables in line with the project plan. b. Managing project scope and change control and escalating bug where necessary. c. Training/ Review of validation protocol/ written report d. Ensuring the availability of data for the system inventory and configuration management. e. Providing adequate resources to support the system validation. f. To witness Qualification activeness. g. Reviewing assessment/inspect reports, responding to findings and taking appropriate actions to ensure GxP compliance. h. Assist during Testing and Manage hand-over of completed Project. |
| Quality Assurance | a. Review and approving of procedures and other validation deliverables b. Providing Quality Assurance and Regulatory expertise. c. Developing grooming material and delivering training on regulations and corporate standards. d. Auditing reckoner systems together with the organisation possessor for compliance with procedures. eastward. Release of the computerized organisation for utilize in alive environment. |
| Project Squad : | a. Members shall come from all departments that. are afflicted by the arrangement. b. As a minimum requirement, representation is necessary from the users, Quality Assurance and Information Technology c. For each team member a back-up shall be identified, mitigating the adventure of unavailability of core members. A list of core members and the backup shall be created and maintained with the system owner. d. The Project squad members shall represent their departments. e. Attend all team meetings or arranging for a substitute. f. Collect and provide inputs for take a chance assessment. k. Reviewing project plans h. Developing and reviewing procedures. i. Reviewing test and validation protocols and other validation deliverables. |
| IT Section: | a. Overall technical responsibleness for the projection. b. Lay down specifications for software, hardware and computer systems. c. Assisting the team in identifying and selection of arrangement vendors. d. Maintaining hardware and software inventory for computer systems. east. Qualifying the infrastructure. f. Providing technical expertise for risk assessment for networked and 'interfaced systems. thousand. Grooming and review of documentation for network infrastructure. h. Developing and maintaining security controls. i. Coordination with Vendors for support and maintenance j. Setting upward controls for server admission to user groups and vendors. |
| Supplier | a. Suppliers tin can exist vendors of commercial systems, companies that develop software on a contract basis, internal software development resources or a combination of the iii categories. b. Responsibilities include developing software and computer systems according to documented procedures. c. Providing documented show that the software has been developed in a Quality Assurance surroundings and tested during development. d. Allowing users to audit the development procedure or the testing procedure. e. Developing and providing functional specifications for the software and computer organisation. f. Offer services to assist users in specifying, installing and validating the organisation. g. Offer support in instance the user has a problem with the system. h. Informing users on critical software errors and workaround solutions and cosmetic action plans. i. Maintaining version control of the lawmaking. j. Informing users on new versions, For example, what is new and how the change tin touch on the validation state touch on the validation state. |
| Validation Agency (if any) | a. To provide 3rd party validation services b. Preparation of Validation Plan, if required c. Training of Risk Assessment Plan d. Carrying Functional Risk Assessments east. Developing and execution of Installation/Operational Qualification & Performance Qualification (wherever required) Protocols for Process Control Systems. f. To provide Validation Summary Written report and Requirement Traceability Matrix for Procedure Control Systems. |
- Other Individuals and groups shall be identified, equally necessary, by the Process or organisation owner, to aid in various activities where their area of expertise will facilitate the evolution and execution to assure the quality of the validation effort. A person can be utilized in more than ane part listed higher up as per requirement.
- IDENTIFICATION AND CATEGORIZATION OF COMPUTERIZED SYSTEMS:
- Identification of Computerized Systems:
List of Computerized Systems including legacy systems that are used or planned to be used at individual unit of measurement shall be prepared.
The list shall exist prepared as per Annexure-I. The list shall include necessary information of system like Name of the System, version number, Location, Application or Use, Criticality i.due east. GxP / Not GxP and Remarks, if any. GxP / Non GxP function shall exist entered in the list afterward assessment of the system as per Annexure-II.
- System Criticality Assessment:
All systems shall be assessed at the initial stage of the project to determine whether it is Quality Critical, Business Critical or has no impact on Quality or Business. Assessment squad shall essentially include members from various disciplines like Procedure Owner, Arrangement Owner, User section, IT, Engineering, Quality Assurance. Other member may be included equally required. The Assessment can be washed as per Annexure-II. Later the assessment, conclusion shall be drawn to identify that the system belongs to ane of the following 2 categories:
-
-
- GxP System: Quality and Business organisation Disquisitional System
-
The systems tin can be termed as GxP System when information technology tails under anyone of the following areas;
- The system has an bear on on patient safety and product quality and data
- The system is used for performing and supporting GxP regulated
- The system maintains and supports business critical information.
- Non GxP Organization:
The system tin be termed as non GxP system when it tails in all the post-obit areas;
- The organization does not take an impact on patient safety and production quality and information integrity.
- The system is not used for performing and supporting GxP regulated
- The organization does not maintain and support business organisation critical information.
- GAMP five; Organization Categorization:
All GxP systems (as per above assessment) shall farther be categorized as per GAMP 5.
For complex systems dissever categorization may exist carried out for different components modules.
- Software Category (As per GAMP v):
Category 1: Infrastructure Software:
Infrastructure elements linked together to form an integrated surroundings for running and supporting applications and services, i.e. software used to manage the operating surround.
For example; Operating Systems, Database engines, Programming languages etc.
Category 3: Non-Configured Products:
This category includes off-the-shelf products used for business purposes. It includes both, systems that cannot be configured to conform to business concern processes and systems that are configurable but for which simply the default configuration is used.
For example; Firmware based applications, COTS, Instruments etc.
Category four: Configured Products:
Configurable software products provide standard interfaces and functions that enable configuration of user specific business processes. This typically involves configuring predefined software modules.
For example; SCADS, PLC, DCS, BMS etc.
Category 5: Custom (Bespoke) Applications:
These systems or subsystems are developed to meet the specific needs of the regulated company. Software is custom designed to accommodate the business process.
For case; Internally and externally developed IT applications/ procedure command systems, Custom ladder logic, Custom firmware etc.
- Hardware Category (Every bit per GAMP5):
Category ane: Standard Hardware Component
These are standard hardware components which are commercially available and no customization is made.
Category ii: Custom Built (Bespoke) Hardware Component
These are hardware components which are configured on standard hardware or customized as per requirement.
The following decision tree tin be used as a guide in determining the applicability of computer organisation validation to a item computerized system;
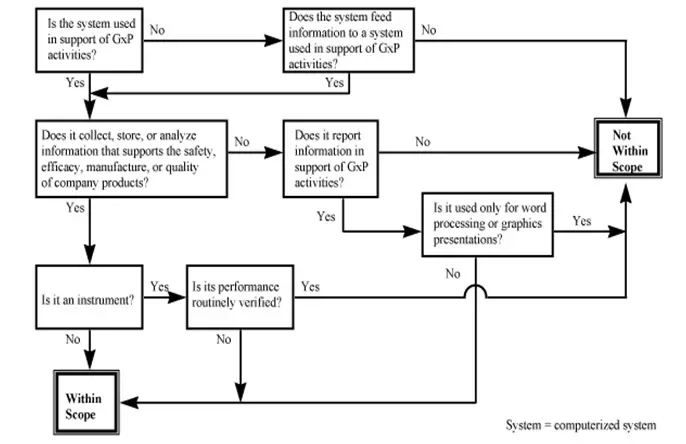
- VALIDATION STRATEGY AND DELIVERABLES:
Validation of reckoner system shall be carried out to ensure that all estimator systems within the organization are developed, installed and implemented in a systematic mode, performing every bit intended and to ensure that the systems are being maintained in a state of control throughout the life cycle in compliance with applicable GxP regulations.
Estimator systems which are integrated with equipment for control, monitoring, operation and/ or' recording shall exist qualified forth with the equipment qualification to have a complete operational and functioning check.
| GAMP Category | Software Type | Examples | Suggested Validation Arroyo |
| 1 | Infrastructure Software (Layered software, Software used to manage the operating environs) | a. Operating systems b. Database engines c. Middleware d. Programming languages due east. Statistical packages f. Network monitoring tools 1000. Scheduling tools h. Version control tools | · Record Version (including service pack), verify correct installation by following approved installation procedure |
| 3 | Not-configured Software (Run-time parameters may exist entered and stored, but the software cannot exist configured to suit the business organization procedure) | a. Firmware based applications b. COTS c. Instruments | · Abbreviated Lifecycle approach · URS · Risk based arroyo to supplier assessment · Record version (and configuration of environment) and verify right installation. · Chance based tests against requirements as dictated past use (for elementary systems regular scale may substitute for testing) · Procedures in place for maintaining compliance and fitness for intended utilise. |
| four | Configurable Software Packages (Software, often very circuitous, that can exist configured by the user to meet the specific needs of the user's business concern process, software lawmaking is not altered) | a. DAS b. SCADA c. PLC d. DCS due east. BMS or EMS | · Life bicycle approach · Take a chance based approach to supplier cess. · Record version number, verify correct installation · Risk based testing to demonstrate applicable works every bit designed in a test surround and within the business process. · Process in place for maintaining compliance and fitness for intended employ. · Procedures in place for managing data. |
| five | Custom (Bespoke) Software (Software custom designed and coded to arrange the business process) | a. Internally and externally adult IT applications/ process control systems b. Custom ladder logic c. Custom firmware | Same as configurable, in addition: · More rigorous supplier cess. · Possession of full life cycle documentation · Design and source code review |
- Life Cycle Model
The validation for process control system shall be carried out as per GAMP 5 guidelines using system implementation life cycle arroyo (defining activities in a systematic way from agreement requirements to system retirement). The validation documentation shall encompass life bicycle management approach for all procedure control systems.
The validation exercise volition follow the typical '5' diagram approach as advocated by GAMP 5. The diagram is shown beneath as reference:
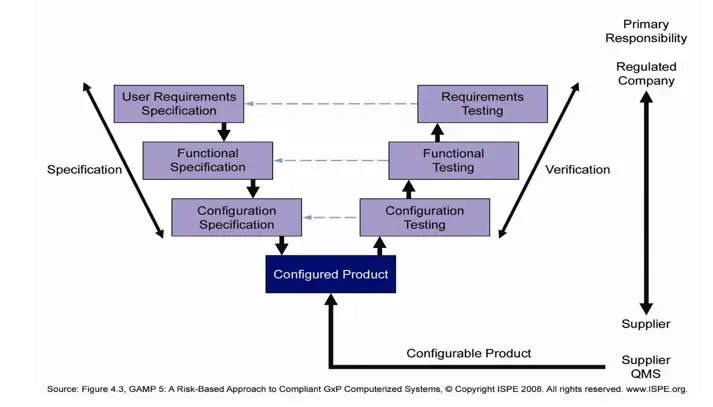
This model comprises of User Requirement Specifications (URS), Functional Specifications (FS), Configuration or Pattern Specifications (DS), configuration testing of code, Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ). A typical life cycle management model is shown in diagram below.
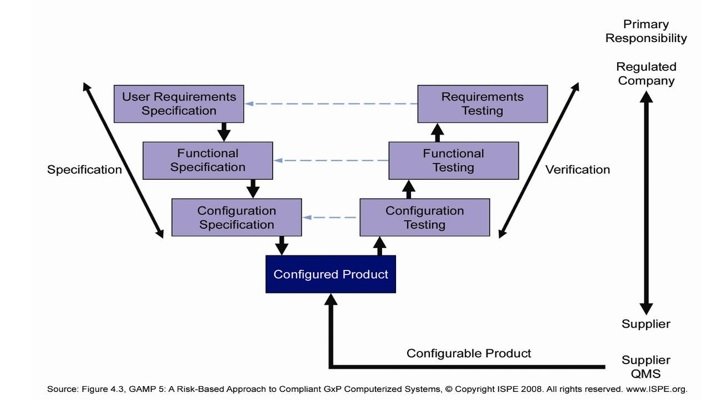

The model suggests that later completion of first validation do, the Process Control systems shall exist governed past formal change control process during performance stage. All changes shall follow the 'V' model depending upon the impact assessment. Subsequently completion of employ of the organisation, the same volition be retired following a divers retirement programme.
Validation using approved validation protocol and reports shall likewise be performed for software and programs where calculations are carried out. For example, calculation of Standard deviation, Mean, Minimum and Maximum value, Relative standard difference, Weight variation programs adding of percentage etc.
The revalidation shall be done if in that location is any revision or updation of software.
Such programs and files shall be individually countersign protected for regular usage.
Following validation strategy shall be adopted for the GxP Systems:
Validation deliverables shall include the requirement specifications, Qualification and validation protocols, adventure assessment and strategies for contingency planning, information dorsumupwards and system security along with others stated in the next point. For GxP systems, all deliverables shall exist listed at initial phase of the validation plan and verified for completeness and correctness afterwards completion of all activities.
The depth and scope of the validation depends on the category of the System components and the complexity & criticality of the application. If any of these deliverables are not considered in the validation cycle, the aforementioned shall be justified.
- For GxP Arrangement:
- For New Systems: Based on take chances assessment, criticality and category of the
hardware, software and other components of the arrangement, Qualification and Validation strategy shall be developed. The strategy and deliverables shall typically exist as follows:
- Proposal and Approving of Change
- Validation Programme (CSVMP shall be considered as validation program)
- Risk Assessment at various stages of the life wheel.
- Training Plans and Training documentation at various stages
- Supplier Cess/ Supplier Understanding
- User Requirement Specification
- Traceability Matrix
- GxP Assessment
- Functional Design Specification
- Installation Qualification
- Operational Qualification
- User Manuals, training guides from Vendor.
- SOPs for the Usage, maintenance, backup, concern continuity plans
- Operation Qualification
- Postal service Implementation review
- Periodic review or verification
- For Legacy Systems:
Validation of, in use legacy systems shall follow the same principles as new systems with some exceptions. Whatsoever updation to legacy systems shall follow the change command process and the validation strategy every bit the new systems.
- For Non GxP System:
The Validation strategy for non GxP system shall be decided past the Projection Team and Users. Yet the minimum requirements to be followed are
- User Requirement Specification
- User Acceptance test
- Training
- Standard Operating Procedures
- SUPPLIER ASSESSMENT:
Supplier assessment is aimed to assess the calculating surround, technology used and quality management organization followed to develop the proposed organization is acceptable and to ensure that the proposed arrangement components conform to the Quality Requirement defined past the organization.
- Company shall consider formally assessing each supplier of GxP 'regulated computerized systems and services.
- Typical supplier assessment activities include but not express to:
- Verification of supplier history.
- Collection of industry feedback.
- Assessment through Questionnaire (postal audit) or Vendor audit (site audit).
- Typically, a basic cess is sufficient for lower bear on systems, while higher impact systems may crave formal audits. Postal audit may be appropriate for suppliers of standard and configurable products and services.
- The competence and reliability of a supplier are key factors when selecting a product or service provider.
- Formal assessment of the supplier shall be done every bit per SOP
- Documentation supplied with commercial off-the-shelf products shall be reviewed past regulated users to bank check that user requirements are fulfilled.
- When third parties (e.g. suppliers, service providers) are used eastward.g. to provide, install, configure, integrate, validate, maintain (e.g. via remote access), modify or retain a computerized system or related service or for information processing, formal agreements must exist betwixt the manufacturer and any third parties, and these agreements shall include clear statements of the responsibilities of the third political party. Information technology-departments shall be considered analogous.
- QUALITY Run a risk MANAGEMENT:
Risk management shall be practical throughout the lifecycle of the computerized system taking into business relationship patient safety, information integrity and product quality. As part of a risk direction organisation, decisions on the extent of validation and data integrity controls shall be based on a justified and documented hazard assessment of the computerized system.
- Principle of Adventure Assessment: The evaluation of the risk to the quality shall be based on scientific knowledge and ultimately linked to the protection of patient. The level of effort, formality and documentation of Quality take chances direction process shall be directly related to the level of risk.
- The five stride take a chance management process has been designed such that information technology may be scaled according to gamble, complexity and novelty of private systems, with each step of the process building upon the previous output;

- Adventure Management shall exist washed based on agreement of following:
- Touch on of the figurer system on Patient Safety, Product Quality and Data Integrity.
- Impact of proposed system on existing organisation, procedures etc.
- Probability of occurrence
- User Requirements
- Regulatory requirements
- System complexity and novelty.
- Supplier and system capabilities
- For tools to be used for risk assessment
- VALIDATION REQUIREMENTS:
- Validation of computer system shall be performed co-ordinate to the validation process.
- Qualification or Validation can be performed either by a Validation team or by an approved external agency.
- When the software application meets the following prerequisites, the validation activities for various units and locations can be clubbed together and carried out centrally by ensuring that all variables in the business concern processes are considered during Performance Qualification.
- The Awarding is managed centrally for all sites.
- It has a unmarried database for all sites
- The hardware is qualified
- Network is Qualified
- The Software application is being used over LAN or web with firewalls for security.
Note: The above requirements may vary instance to example basis.
- If the above listed prerequisites are non met, the validation exercise will exist carried out separately (if required).
- However grooming of Users and post implementation review shall be done through change control process.
- DOCUMENTATION:
Documentation office plays a vital role in overall life bicycle of Figurer organisation in user and regulatory perspective. It provides evidence to reviewer and data to finish users. The validation documentation and reports shall comprehend the relevant steps of the life cycle. Manufacturers shall be able to justify their standards, protocols, acceptance criteria, procedures and records based on their gamble assessment.
Validation documentation shall include change command records (if applicable) and reports on any deviations observed during the validation process. Information technology shall exist ensured that the system has been developed in accordance with an appropriate quality management organization.
- All documents (where ever feasible) shall take unique identification number and version control.
- All documents shall be clear, legible and well defined.
- Change in whatsoever validation activity from the initial plan (if any) shall exist documented equally per Change control process and can be attached as amendments to the respective validation certificate.
- Each validation activity executed shall be recorded and signed by individuals and groups involved.
- Proofs of validation and related activities carried out, such every bit screen shots, calibration certificate, grooming records etc. (where applicative), shall be retained with corresponding documents.
- All documents shall be retained as per Document Data control process.
- The documentation requirements for the deliverables shall be met. If any of the deliverable is not planned for the validation cycle, the same shall be justified in the individual validation plan.
- Traceability Matrix:
A traceability matrix shall be prepared equally per Annexure-III (or as per validation agency document) to ensure that all requirements are met and related documents can be traced immediately throughout the life bike.
Traceability matrix shall ensure the following
- Requirements are met and can exist traced
- Requirements are verified.
- Enables easier document identification.
- System DESCRIPTION:
An up to date system description detailing the physical and logical arrangements, data flows and interfaces with other systems or processes, whatsoever hardware and software pre-requisites, and security measures shall be available. It shall include at least following contents:
- Purpose of the System
- Main Organisation role
- Regulatory Impact
- Computing Surroundings
- Organisation Component
- Organisation Interfaces
- Access and Security Control
- Actions in example of Failure
- Electronic Records & Signatures (If applicable)
- Category of the Computerized System and Justification.
- Glossary
An updated system description shall exist maintained throughout the life cycle of organisation equally per Annexure- Iv.
- User Requirement Specification:
The User Requirement Specification is a detailed document which is written by the Users and describes the required functions of the computerized organization and shall be risk based and GMP affect based.
The user requirements specification shall be used as the ground for the development of the system acceptance examination procedures {Performance Qualification examination protocol. User requirement shall specify "WHAT is REQUIRED". The requirements shall be Complete, Unambiguous, verifiable, traceable, articulate' and consistent. The User requirement shall specify the minimum hardware and Operating organisation for installation of awarding software. For application software, detailed requirement of the controlling attributes such as countersign command, access level, and security system and information direction shall exist specified.
URS shall be prepared as per
Typical URS shall comprise simply not limited to or as appropriate
- Operational requirements
- Functional requirements
- Information requirements
- Technical requirements
- Interface requirements
- Surroundings requirements
- Performance requirements
- Availability requirements
- Security requirements
- Maintenance requirements
- Regulatory requirements
- Migration requirements
- Life cycle requirements
- Functional Design Specification:
For complex Process Control Systems a functional pattern specification may be issued. The certificate includes technical details on the functions & design of the arrangement. The Functional Design Specification defines how the requirements outlined in the URS are implemented. This documents links Installation and operational qualification, which tests design and function respectively. FDS is normally written by the Vendor and reviewed and approved by user.
Bespoke systems will require a full FDS whereas commercial off-the-shelf systems (COTS) will crave a much simpler FDS.
FDS shall be prepared every bit per Annexure-VI.
- Installation Qualification (IQ):
The Installation Qualification (IQ) is the process of demonstrating that the system components accept been installed according to the manufacturer'due south specifications and that all deliverables are properly deemed for IQ protocols shall exist developed on the basis of agreement of the system, URS, Software blueprint specification and System provider'due south recommendation and shall draw how organisation components shall be installed. The IQ is achieved by documenting all installation activities carried out to ensure it meets the acceptance criteria defined in the protocol.
Installation Qualification Protocol/ Report shall be prepared as per Annexure-VII.
- Operational Qualification (OQ):
The Operational Qualification (OQ) is a test of the functions to ensure that each component of a computer system performs as intended (predefined specification) inside representative or anticipated operating ranges.
Operational testing shall be carried out as per approved OQ protocol which shall be adult by the Validation team, reviewed and canonical by QA.
In sure cases, the executed Operational Qualification documents tin be taken from the vendor and reviewed by the validation team members for acceptance.
- OQ protocols shall be developed with consideration of following:
- Company policies and procedures
- Results of take a chance assessments carried out.
- Results of supplier assessment.
- Functional pattern specification.
- The level of system components as per GAMP 5.
Operational Qualification Protocol/ Written report shall be prepared as per Annexure-VIII.
- Performance Qualification (PQ):
Performance Qualification shall follow successful completion of Installation Qualification and Operational Qualification. The Performance Qualification (PQ) ensures that the full system performs as intended in the specified operating range. The total system includes all hardware and software components, associated equipment, people and procedures that make upwards the system. The execution process is conducted using specific pre-divers dataset or bodily live data.
Computerised systems exchanging data electronically with other systems shall include appropriate congenital-in checks for the correct and secure entry and processing of information, in order to minimize the risks.
Performance Qualification Protocol/ Report shall be prepared as per Annexure-Ix.
- Validation Protocol & Report:
Validation protocols & reports (FDS, IQ, OQ & PQ) shall be prepared in-house or Vendor certificate can too exist used, as it is, if fulfilling the regulatory and customer requirement. Documents for External Validation Agency can too be accepted.
- Numbering Arrangement for Qualification Documents
The numbering system which shall be used for all documents related to Qualification and Validation shall be numbered as:
"Thirty/CSV/YYY/ZZ-NN" Where,
"Xxx" stands for Certificate Code mentioned as below tabular array (may be of 2 or three characters)
| Document Name | Document code |
| Traceability Matrix | TM |
| GxP Cess Checklist | GAC |
| Functional Design Specification* | FDS |
| User Acceptance Test | UAT |
| Installation Qualification Protocol | IQP |
| Installation Qualification Report | IQR |
| Operational Qualification Protocol | OQP |
| Operational Qualification Report | OQR |
| Functioning Qualification Protocol | PQP |
| Functioning Qualification Written report | PQR |
| System Description | SD |
*Equipment/ Instrument/ System Design Specification Sheet (DSS) may also be considered as per SOP wherever applicable.
"/" forward slash as separator.
"CSV" stands for Calculator System Validation
"/" forward slash as separator.
"YYY" stands for Equipment / Instrument/ System code.
"/" forward slash as separator.
"ZZ" stands for serial number starting from 01 for individual Equipment / Musical instrument / System code.
"-" stands for dash as a separator.
"NN" denote revision number of document which shall start from "00" and shall modify later on every revision every bit 01, 02 and and then on.
e.thou. Document numbering for installation qualification of RMG shall exist done every bit:
Installation Qualification Protocol IQP/CSV/RMG/01-00
Installation Qualification Report IQR/CSV/RMG/01-00
NOTE: 1. At the time of requalification revision number of the certificate shall be increased as 01, 02 and so on.
- Whenever the grouping of Equipments/ Instruments/ Systems consider for qualification / requalification denotes the equipment code as EQ.
- For uncomplicated systems integrated with the equipment, may be qualified forth with equipment qualification defining the exam strategy.
- Qualification Summary Report:
For complex computer systems, after successful completion of qualification activities a summary written report may be prepared by a Validation team. The summary study shall include this data
- Whether or not the qualification steps were followed
- Whether or not the expected results were attained.
- Description of any divergence from expected results
- Follow-upwards activities to correct any deviations
- Statement of whether the overall qualification objectives are met and organisation can / cannot be used for further awarding.
- Mail Implementation Review:
Post implementation review shall be carried out through change control process. During this review period, post go alive malfunctions shall be monitored and reported through Maintenance/Breakdown Work Social club or Deviation handling (or Non-conformance treatment procedure and whatsoever changes through Alter Management System These malfunctions or issues shall be classified equally small-scale/ major, software issues, training issues, and Procedural issues while investigation. The corrective action program for these issues shall exist implemented by having software' corrections and evaluations, Training to users and procedural updation.
Wherever the software replaces a manual operation, it is recommended to continue performing the manual activity in parallel to the software implementation during this stage.
For critical information entered manually, there shall exist an additional check on the accuracy of the data. This cheque may be done by a second operator or past validated electronic means. The criticality and the potential consequences of erroneous or incorrectly entered data to a organisation shall be covered by take a chance management.
- Arrangement Handover :
Afterward successful completion of qualification, provisional/ last handover of system shall be carried out. Handover certificate shall be prepared every bit per Annexure-Eleven, or information technology may be included in validation study or acceptance criteria.
- Periodic Review:
Periodic review shall be carried out throughout the life of figurer system to verify that the organisation remains compliant with relevant GxP requirements, fit for its intended use.
An annual review period is recommended. The review shall include, merely shall not be express to, the current range of functionality, changes, deviation records, incidents, bug, upgrade history, functioning reliability, security and status reports for validated country etc.
The results of the review are documented in a Periodic Review Report (every bit per Annexure-X) which will conclude either that the validation status is upheld or that revalidation is required.
- Requalification and Revalidation:
The extent of qualification and validation activities and test to be carried out in both cases shall be based on outcome of periodic review, criticality of the system and risk involved.
Validation schedule/ planner for applicable systems shall be in identify at individual site which need to exist prepared as per Annexure-V. Any change to this schedule/planner shall be recorded. Revalidation or requalification should cover all aspects of equipment's and its decision-making application.
Requalification and Revalidation is of 2 types:
- Requalification and Revalidation subsequently change:
Estimator System shall exist subjected to Requalification/ Revalidation subsequently assessment of changes fabricated to the existing system components and supporting systems etc.
Complete Qualification/ Validation of the systems shall be considered when changes fabricated can have impact on the product Quality, patient safety and data integrity or the production characteristics.
Partial or reduced Qualification/Validation of the systems shall exist done when changes made can accept limited touch. Justification for Partial or reduced Qualification / Validation shall be available.
- Periodic Requalification and Revalidation:
Recommendation for Periodic Requalification and Revalidation of the organisation shall be fatigued based on periodic review of the software. Information technology shall aim at ensuring that the system is continuing to perform as intended. Revalidation of the computerized systems shall be washed at every three years.
Re-qualification of instruments shall non be performed. Instead, periodic calibration, system suitability (as applicable) and almanac maintenance (i.e. AMC) shall be carried out to verify the performance of the instruments.
- Modify Command:
Any changes to a computerized organization including system configurations shall only be made in a controlled manner in accordance with a defined process.
- Procurement and implementation of any new arrangement or any modify in the existing system component shall be handled through Change Control process
- All changes to the figurer system shall be evaluated for their bear on on the organization and to the Organization lifecycle documentation.
- The changes to any computerized system or hardware shall be done afterwards ensuring fill-in of the applications, data etc.
- The changes shall be primarily done on the test surround and if found successful shall exist extended to the alive surround.
- The extent of verification and validation shall exist run a risk based depending on type of alter and its impact on Product Quality, Patient safety and Data integrity.
- TRAINING:
For successful implementation, maintenance and operation of whatever system, training shall be conducted at various stages of life cycle. Training plan shall exist prepared for private System as per requirement and shall cover all user groups. The type and extent of grooming shall be based on office and responsibility of each user group.
Preparation for any new computerized system shall be provided by the software developer during the initial phase for individuals from Data Technology and Procedure possessor, Arrangement Owner along with the core grouping.
The trained grouping shall be farther responsible for preparation the remaining users at various stages of the life bicycle.
Retraining shall exist conducted as and when required based on evaluation of grooming needs of the users along with sit-in. The new entrants shall be trained by the existing users of the computerized arrangement preferably on the test environment. For detailed procedure of Training
- MAINTENANCE AND SUPPORT:
- Preventive Maintenance:
Preventive maintenance shall ensure polish and reliable performance on a mean solar day-past-day ground. Activities shall include: Regular removal of temporary files from the hd. Regular virus checks of systems that are connected to a network and/or to the Net, regular checks for hardware and software.
- Backup and Restore:
Operating software, application software, configuration settings and data shall exist backed up on external media to ensure access, if on-line records are lost either through accidental deletion or equipment issues
Backup and restore Procedure shall essentially include:
- Back up frequency .
- Storage area
- Storage period
- Storage condition
- Procedure for backup and restore.
- Frequency of backup storage verification
Responsibleness for fill-in and restore shall be with Organisation owner or every bit defined in individual SOP.
If data are transferred to another data format or organization, validation shall include checks that information are not contradistinct in value and/or pregnant during this migration process.
Regular back-ups of all relevant data shall be washed. Integrity and accurateness of backup information and the ability to restore the data shall be checked during validation and monitored periodically.
Support and maintenance activity provided by the manufacturer or third party support vendors shall be onsite to the extent possible.
Remote support and maintenance action tin also be done past the manufacturer or third parties with network controls and gateway securities in place. This activity shall be monitored by the Organization Owners or the IT Support grouping within the system.
- Data storage and Archiving:
The system possessor with the support of Information technology and QA shall develop an archiving strategy for each system as per system requirement. Data generated by the figurer organization shall be regularly removed from the system's hard deejay(due south) and archived to avoid overloading the hard disk(s) and loss of data.
Data storage/ archiving may exist in the grade of NAS/Server, localized arrangement server, hard disk, print. The system not having such options shall be made compliant by developing procedural controls.
Data shall exist secured past both concrete and electronic means confronting damage. Stored information shall be checked for accessibility, readability and accuracy. Access to data shall be ensured throughout the memory menses. Data may be archived. This information shall be checked for accessibility, readability and integrity.
If relevant changes are to exist made to the system (due east.g. calculator equipment or programs), so the ability to recollect the data shall exist ensured and tested.
- Contingency Program and Disaster Management:
Contingency plan and disaster direction procedure shall be prepared because impact on patient safety, data integrity and production quality in instance of a system failure or a disaster. Responsibility for contingency plan and disaster management shall be with IT Administrator and system owner. This information shall exist checked for accessibility, readability and integrity.
For the availability of computerized systems supporting disquisitional processes, provisions shall be made to ensure continuity of back up for those processes in the issue of a system breakdown (e.g. a manual or alternative system). The time required to bring the alternative arrangements into employ shall be based on adventure and appropriate for a particular organisation and the business concern process it supports. These arrangements shall exist adequately documented and tested.
- Security and User Administration:
System security is important to ensure confidentiality, authenticity and integrity of data. In full general, Process for the security organisation shall be prepared and followed for Security in Computerized Systems and User Management respectively.
Wide Surface area network (WAN), if any is provided by It department. Firewall and router is installed for protection of any external threats. All the applications are running on the intranet and are not accessible outside Network.
For back up the access is being provided to Vendors using remote command tools which have the provisions to restrict or allow view merely and total access. This is always done in supervision of the IT Engineers and the Organisation Owner. The changes are controlled by the Organisation owners.
Whatever updates/patch or changes to applications should undergo the modify control process
Notwithstanding separate procedures tin exist developed for different computer systems by the system owner with the support of IT and QA, if required
The Security and User Management Procedure for a specific system is in based on the criticality of the organization and the system functions and chance assessment. Concrete and logical security to limit access to the systems may be considered. Suitable methods of preventing unauthorized entry to the system may include the apply of keys, laissez passer cards, personal codes with passwords, biometrics, restricted admission to computer equipment and information storage areas. The extent of security controls depends on the criticality of the computerized organisation. Creation, alter, and cancellation of admission authorizations shall exist recorded. Management systems for information and for documents shall be designed to record the identity of operators entering, changing, confirming or deleting data including date and time. The spreadsheets used for critical adding to be validated every bit per SOP and shush canvass should be secure to avoid unauthorized admission.
- Document COMPLETION Procedure:
Each computerized arrangement shall accept a document completion procedure divers in the Standard Operating procedure which shall include but not be limited to;
- Electronic Records:
It shall be possible to obtain clear printed copies of electronically stored data which tin can be stored and archived for the retention period of the certificate.
- Audit Trails:
Consideration shall exist given, based on a hazard assessment, to building into the system the cosmos of a record of all GMP-relevant changes and deletions (a organization generated "inspect trail"). For change or deletion of GMP-relevant data the reason shall exist documented. Audit trails need to be bachelor and convertible to a generally intelligible form and regularly reviewed.
- Incident Management:
All incidents, not merely organization failures and data errors, shall exist reported and assessed. The root cause of a critical incident shall exist identified and shall class the footing of corrective and preventive actions. At that place are different QMS tools to identify, log, investigate, evaluate/empathise, correcting discrepancies (while attempting to prevent their recurrence) and for recognizing potential discrepancies (to forbid their occurrence)
- Electronic Signature and its controls:
All electronic records should have a handwritten review and approval bicycle or an electronic signature. Electronic records may be signed electronically. Electronic signatures are expected to:
- take the same touch on equally hand-written signatures within the boundaries of the company,
- be permanently linked to their respective record,
- include the fourth dimension and date that they were practical.
The electronic signatures shall follow the security norms to avoid misuse and sharing.
- SYSTEM RETIREMENT:
System retirement for individual computer system shall be made. System retirement programme shall be prepared based on the risk involved and impact on other business process. System retirement plan shall essentially include following:
- Cess of impact on interfaced systems.
- Deactivation of organisation (hardware/software/ network).
- Disposal of software and hardware.
- Retentiveness and controlled access of celebrated information for reference.
- Migration of data to any proposed new organization when the data is compatible to the flew system. (Migration process shall be accurate, complete and verifiable).
- Documentary evidence of each activeness listed above.
- PROJECT ACTIVITIES MONITORING, Controlling AND REPORTING:
Project activities, tasks and their responsibilities shall be as per the Validation Master Programme. Projection calendar shall be prepared to provide target time lines of each project action and provision shall exist available to record actual activity completion date. Issues shall exist tracked to manage resolution details and approval activities. Open up bug shall be discussed equally needed during project meetings. In add-on, a project consequence log, consisting of the effect, number and date, assignee, and resolution, shall be distributed to the project team members as necessary.
Squad meetings shall be conducted to talk over progress, issues, and plans for the project. Meeting minutes or equivalent advice shall be made available to team members. This VMP and the validation documentation outlined above shall exist created and stored for complete life cycle of the proposed system.
- REFERENCES:
- GAMP5: Good Automated Manufacturing Practices 5: A Risk-Based Approach to Compliant GxP Computerized Systems. International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering (ISPE); 2008.
- 21 CFR Part xi
- EU GMP Annex 11
- Motion picture/S guide to good manufacturing practice for medicinal products annexes: Annex 11 – 1026 Computerised systems.
- WHO Technical Report Series, No. 937, Annexure iv, Appendix v
- MHRA GMP data integrity definitions and guidance for industry.
- ANNEXURE:
| Annexure No. | Title |
| Annexure-I | Listing of computerized/ automated systems |
| Annexure-2 | GxP Assessment Checklist |
| Annexure-III | Traceability Matrix |
| Annexure-IV | Organization Description |
| Annexure-Five | Computerized/ Automated System Re-validation / Re-qualification Planner |
| Annexure-Half-dozen | Functional Design Specification |
| Annexure-Vii | Installation Qualification Protocol/ Report |
| Annexure-Viii | Operational Qualification Protocol/ Report |
| Annexure-9 | Performance Qualification Protocol/ Written report |
| Annexure-10 | Periodic Review Report |
| Annexure-XI | Handover Certificate |
| Annexure-XII | User Acceptance Test |
- ABBREVIATIONS:
| Terms/ Abbreviation | Definition/Expanded Form |
| COTS | Commercial off the shelf |
| URS | User Requirement Specification |
| FDS | Functional Design Specification |
| DQ | Design Qualification |
| IQ | Installation Qualification |
| OQ | Operational Qualification |
| PQ | Performance Qualification |
| U.s.a. FD& C | United Land Food, Drug and Corrective Deed |
| United states of america PHS | United State Public Health Service |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| EU | European union |
| GMP | Practiced Manufacturing Practice |
| API | Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient |
| GCP | Skillful Clinical Practice |
| GLP | Skillful Laboratory Practice |
| GOP | Practiced Distribution Do |
| GQP | Practiced Quality Exercise |
| POMA | Prescription Drug Marketing Act |
| HSE | Wellness, Safety and Environs |
| Information technology | It |
| QA | Quality Assurance |
| SOP | Standard Operating Procedure |
| LAN | Local Surface area Network |
| VMP | Validation Primary Program |
| WAN | Wide Area Network |
| GAMP | Good Automated Manufacturing Practices |
| CSVMP | Computer Organization Validation Master Plan |
| QMS | Quality Direction System |
- Document History:
| Alter Control Number/ Document Amendment Number | Reason for Revision | Superseded Document Number | Effective Appointment |
| New Certificate | Nada |
Annexure-I
List of computerized/ automatic systems
Department:…………….. Effective Date:……………………… Revision No.:……………….
| Sr. No. | Name of the Arrangement/ Equipment/ Instrument | Organisation/ Equipment/ Musical instrument ID | Version number/ Code No. | Location | Application of utilize | GxP/ Not GxP | Software Category (as per GAMP5) | Remarks |
| Prepared Past (Sign/Date) | Checked By (Sign/Date) | Reviewed By (Sign/Date) | Canonical By (Sign/Appointment) |
| Executive/ Designee-Concerned Section | Head/ Designee-Concerned Department | Head/ Designee-QA | Caput /Designee-Quality |
Note: This format shall be used in soft form.
Annexure-II
User Requirement Specification
Document No.:………..
| Sr. No. | Organisation/Equipment/ Instrument Name | Arrangement/ Equipment ID | Make/ Model | Equipment Series Number | Room Number |
| Intended use: | |||||
| Sr. No. | System GxP Criteria | Yes/No | Remark |
| ane. | Is the organization used to monitor, command, or supervise a GxP drug manufacturing or packaging procedure? | ||
| 2. | Is the system used for GxP batch or batch records? | ||
| iii. | Is the system used for GxP belittling quality control? | ||
| 4. | Is the system used to monitor, control, or supervise warehousing or distribution with a GxP implication? | ||
| 5. | Does arrangement affect regulatory submission/registration? | ||
| 6. | Does system perform calculation/algorithms that will support a regulatory submission/registration? | ||
| 7. | Is organisation integral part of equipments, instrument, used for processing/ testing/ release/ distribution of the product/samples? | ||
| 8. | Does the arrangement perform functions critical to personnel safety? | ||
| 9. | Does the system dispense information or produce reports to be used past GxP quality related determination authorization/approval processes? | ||
| x. | Does system define materials (i.e., raw materials, packaging components, conception) to be used? | ||
| 11. | Will organization to exist used to support product release? | ||
| 12. | Does organisation deal with resource allotment identification code for raw material, formulated products, or package components? | ||
| 13. | Does system employ whatever electronic signature capabilities or provide the sole record of signature on a document subject to review by regulatory agency? | ||
| 14. | Does the organisation have any impact with respect to patient prophylactic or Product quality or business criticality? | ||
| If answer to all questions is 'No', then arrangement is Non- GxP System. If reply of anyone above question is 'YES', and so Arrangement nether assessment is GxP organization. | |||
| Listing each individual software controlled sub-arrangement; along with software categories. (Include all software categories.) | |
| Sub-system (PLC, HMI etc.) | Category |
Conclusion: Based on above assessment, information technology tin can be concluded that the system under consideration is GxP I Non GxP Organization.
| Prepared Past (Sign/Date) | Checked By (Sign/Date) | Reviewed Past (Sign/Engagement) | Canonical Past (Sign/Date) |
| Executive/ Designee-Concerned Department | Head/ Designee-Concerned Department | Caput/ Designee-QA | Head /Designee-Quality |
Note: This format shall exist used in soft form.
Annexure-III
Traceability Matrix
Document No.:………..
| Requirements of URS | Reference trace points in FDS | Verification plan and traceability | ||||||
| IQ Ref. Md no. | OQ Ref. Physician no. | PQ Ref. Doc no. | ||||||
| URS point no. | Details | Programme | Trace point | Program | Trace point | Plan | Trace indicate | |
.
| Prepared by: | Reviewed by: | Approved by: |
| Validation squad | Quality balls | Head-Quality Balls |
| Date: | Appointment: | Date: |
Annexure-IV
System Clarification
Certificate No.:………..
| Sr. No. | System/Equipment/ Instrument Name | System/ Equipment ID | Version Number |
- Purpose of The System:
- Master System part:
- Regulatory Bear on:
- Computing Environs:
- Organization Component:
- Hardware Requirements:
- Software Requirements:
- Other components(if any):
- System Interfaces:
- Admission and Security Command:
- Actions in example of Failure:
- Electronic Records and Signatures (if applicable):
- Category of Computerised System and Justification:
- GxP / Non GxP :
- GAMP category:
- Category for Arrangement Components:
- Category for Software application
- Justification:
- Glossary:
| Prepared Past (Sign/Date) | Checked Past (Sign/Date) | Reviewed By (Sign/Date) | Approved Past (Sign/Engagement) |
| Executive/ Designee-Concerned Department | Caput/ Designee-Concerned Department | Caput/ Designee-QA | Head /Designee-Quality |
Annotation: This format shall be used in soft course.
Annexure-V
Computerized/ Automated System Re-validation / Re-qualification Planner
| S. No. | Equipment/ System Name | Equipment/ Arrangement ID | Make | Capacity (if applicable) | Location | Qualification Completed on | Requalification Due on |
| 1. |
| Prepared By (Sign/Date) | Reviewed By (Sign/Engagement) | Approved By (Sign/Engagement) |
| Executive/ Designee- QA | Sr. Executive/ Designee- QA | Head/ Designee- QA |
Annexure-VI
Functional Blueprint Specification
Format for Functional Design Specification Certificate-First Folio
Visitor Name______________________________
Functional Design Specification Of__________________________
| Certificate No. | |
| Make | |
| Capacity | |
| Effective Date |
Format for Functional Design Specification Document-2d page onwards
| Title: Functional Pattern Specification of ______________________ | |
| Document Number: | Page Ten of Y |
- Purpose
- Scope
- Responsibility
- System/Equipment Clarification
- Vendor Information
- Functional and Design Specification
- Material of Construction
- Safety Features
- List of back up utilities
- List of the required documents
- Discussion and documentation of warranty: Familiarization, training and other vendor services.
| Detail | Information |
| Time of warranty | |
| Warranty certificate | |
| Discussion on warranty | |
| Vendor Services understanding |
- Reference Documents
- Attachment
- Deficiency and corrective activity
- Summary and conclusion
- Review and Blessing of the Functional Design specification:
Note: Contents can exist modified as per requirement.
Annexure-7
Installation Qualification Protocol/ Report
Format for Installation Qualification Document-Showtime Page
Visitor Name__________________________________
Installation Qualification Of ________________________
| Document No. | |
| Equipment/System Identification No. | |
| Location | |
| Software Designer | |
| Effective Date | |
| Reference Document No. |
Format for Installation Qualification Document-2d folio onwards
| Title: Installation Qualification Protocol/ Written report of ______________________ | Equipment/Organization Tag No.: |
| Document Number: | Page 10 of Y |
- Protocol/ Report Approval
- Purpose
- Telescopic
- Responsibility
- Training of personnel
- Pre-requisite of Installation Qualification
- System/Equipment Description & Identification
- Prophylactic features and alarms
- Installation verification
- Acceptance Criteria
- Deviations and corrective actions
- Abbreviation
- Reference
- Attachment
- Summary and Conclusion
- Certification
Notation: Contents tin be modified as per requirement.
Annexure-VIII
Operational Qualification Protocol/ Study
Format for Functioning Qualification Document-First Page
Company Name____________________
Functioning Qualification Of ____________________________
| Document No. | |
| Equipment/System Identification No. | |
| Location | |
| Software Designer | |
| Effective Engagement | |
| Reference Document No. |
Format for Functioning Qualification Document-Second folio onwards
| Title: Operation Qualification Protocol/ Study of ______________________ | Equipment/System Tag No.: |
| Document Number: | Folio X of Y |
- Protocol/ Written report Blessing
- Purpose
- Scope
- Responsibility
- Equipment/System Description
- Preparation of Personnel
- Pre-Requisite of Operation Qualification
- Operational and Functional Check
- Operation Acceptance Criteria
- Draft SOPs Verification and Training
- Deviations and corrective actions
- Abbreviation
- Reference
- Attachment
- Summary & Conclusion
- Certification
Note: Contents can be modified as per requirement.
Annexure-IX
Operation Qualification Protocol/ Report
Format for Functioning Qualification Certificate-First Page
Visitor Name: _________________________________
Performance Qualification o f ________________________
| Document No. | |
| Equipment/Organization Identification No. | |
| Location | |
| Software Designer | |
| Effective Engagement | |
| Reference Document No. |
Format for Operation Qualification Document-2d page onwards
| Championship: Performance Qualification Protocol/ Report of ______________________ | Equipment/System Tag No.: |
| Certificate Number: | Page X of Y |
- Protocol/ Report Approval
- Purpose
- Telescopic
- Responsibleness
- Preparation of personnel
- Pre-requisite of Functioning Qualification
- Test Program:
- Critical Variable and measuring response
- Examination Parameter and Specification
- Credence Criteria
- Deviations and cosmetic actions
- Abbreviation
- Reference
- Zipper
- Summary and Conclusion
- Certification
Note: Contents tin be modified equally per requirement.
Annexure-Ten
Periodic Review Study
| Sr. No. | System/Equipment/ Instrument Name | Organization/ Equipment ID | Make/ Model | Equipment Series Number | Room Number | Reference Document No. |
Review Points (every bit applicable merely not express to):
- Review of Arrangement Description (as per System description format)
- Review of cumulative and/or repetitive upshot of all changes to include an assessment whether further action is warranted
- Review of all deviations/ Incidents/ Not-Conformances including frequency and reasons to make up one's mind whether at that place is a trend away from qualified state
- Review of advisable maintenance and scale records(every bit applicative) to determine whether there the system has been properly maintained
- Review performing trending, if applicable (east.one thousand. organization logo)
- Review system confronting applicable regulatory, GMP and site requirements established since the terminal periodic review/ qualification.
- Upgrade history
- Performance reliability
- Current range of functionality
- Status of validation documentation and updates
- Status of SOPs and updates
- Status of Qualifications
- Status of Authorizations/ security
- Condition of affected SOPs for the changes
- Training Records (as per the existing Preparation SOP)
Note: The in a higher place data shall be provided by respective section in-charge/designee and finally be compiled by user along with QA.
Conclusion:
| Prepared By (Sign/Engagement) | Checked By (Sign/Date) | Reviewed By (Sign/Date) | Approved By (Sign/Date) |
| Executive/ Designee-Concerned Department | Executive/ Designee-QA | Head/ Designee-QA | Head /Designee-Quality |
Note: This format shall be used in soft form.
Annexure-11
HANDOVER Certificate
This is to certify that the (Name of the system) version (version of the system) has been successfully qualified on (Test/Live Server) and is existence (Finally/Provisionally) handed over for usage On (Engagement)
Qualification performed past Validation Team:
| Sr. No. | Name | Designation -Department | Signature/Appointment |
Canonical by:
| Head- EG | Head –Concerned Department | Head- Quality | |
| Name | |||
| Signature | |||
| Date |
Note: This document can be modified as per requirement.
Annexure-XII
User Acceptance Test
| USER Acceptance TEST OF_______________ | |
| Certificate No.: | Page 10 of y |
Approving PAGE
Compiled by: _________________________________________________________
Validation Team Engagement
Reviewed by: _________________________________________________________
Quality Assurance Date
Approved by: _________________________________________________________
Head- Quality Balls Date
- USER ACCEPTANCE Exam:
| Sr. | Footstep | Acceptance criteria | Observation | Result |
- DEVIATIONS OBSERVED (If Any):
- Conclusion AND RECOMMENDTION:
- USER Acceptance TEST SIGN OFF:
| Compiled Past | Reviewed By | Approved By |
| Validation Team | Quality Assurance | QA Head |
| Date: | Date: | Date: |
More Jobs [email protected] h ttp://pharmaguidances.com
Source: https://pharmaguidances.com/computer-system-validation-master-plan/